Polkadot is a cryptocurrency and a network that is known for the ability to maintain privacy between private and public blockchains while allowing interaction at the same time with a central protocol. By allowing both privacy and interoperability, Polkadot shows the true potential of crypto.
What Is Polkadot? – Definition & Meaning
Polkadot is a blockchain with the core network, known as the “Relay Chain,” where other blockchains connect and communicate. The Relay Chain hosts other blockchains, handling security and transactions. This seamlessly allows cross-chain interoperability.
Polkadot allows not only the sending of its native coin, DOT, across various blockchains, but it also allows them to communicate and exchange data. The concept is that instead of having separate entities that work independently, they would become a part of the same ecosystem where information and money can be exchanged in a secure and scalable way. Private blockchains have somewhat different technical protocols from public blockchains in the ecosystem, but it has several ways to resolve communication between the two distinct types of networks.
Polkadot is flexible and adaptive enough in its architecture to facilitate new technology, enabling developers to take advantage of the scalability, interoperability, and security offered. Furthermore, it has a governance model that allows the blockchain to evolve.
The history of Polkadot
Polkadot has very intertwined history with Ethereum. The founder of Polkadot, Dr. Gavin Wood, was a chief training officer and core developer of Ethereum. He developed Ethereum’s smart contract programming language called Solidity. In October of that same year, he left Ethereum in 2016 to build a more sharded blockchain and published Polkadot’s white paper.
While he was still at Ethereum, he co-founded the company that would eventually be turned into Parity Technologies. The company developed important infrastructure technology for blockchains, such as the Substrate development framework and the Polkadot network.
In 2017, Dr. Wood also co founded the WEB3 Foundation, a nonprofit entity established to support the R&D of Polkadot and oversee its funding efforts.
In July 2017, a hacker managed to exploit a vulnerability in the Parity wallet code and stole 153,000 Ethereum, which was roughly $33 million at the time, from three different wallets.
There was an initial coin offering in October that raised $145 million in just under two weeks, making it one of the largest ICOs in the crypto markets up to that time. However, just a few days after the token sale, Parity Technology experienced a new hacking incident. The ICO smart contracts were hacked, and 66% of the funds raised during the event were frozen. The event ended up being irreversible and slowed down the development.
Polkadot did manage to raise more funds, essentially making up the difference. The development goals ended up being on track, and by 2019, everything was in order.
How does Polkadot Work?
Polkadot provides a core network known as the “Relay Chain” and parallel blockchains called “parachains.” The Relay Chain protocol determines the network’s shared security, consensus, and cross-chain interoperability. The Relay Chain keeps the whole infrastructure together, connecting network participants in providing transaction finality.
The Relay Chain was deliberately built with minimal functionality in mind. Smart contracts are not supported, as the chain is used to provide coordination of the overall ecosystem, including public and private parachains.
Coordinating various parachains allows each sovereign blockchain to have its own tokens and governance, as well as specific case uses. Parachains will use the Relay Chain security and interoperability for the finality of transactions. Using the Relay Chain allows for the parachain’s system to work seamlessly with a solid structure so developers can work on privacy and scalability for their particular applications.
Each parachain can take advantage of one of Polkadot’s most significant benefits, its established security protocol and fast, scalable transaction speeds. Parachains lease lots limited to 100 and Polkadot to participate in the network. Due to space limitations, slot allocation may be somewhat competitive in the future and challenging to obtain. However, Polkadot is already behind the scenes addressing scalability for more slots.
Governance of Polkadot
The term “governance” refers to how transactions and block verification rules are decided in a blockchain and how those rules are implemented and enforced. It sets up a system of norms for the ecosystem that users follow.
Polkadot governance is done through the proof of stake protocol, allowing the majority of the state to control the network. Polkadot’s specific type of proof of stake is a nominated proof of stake, where nominators bank validators with their stake as a sign of trust in their good behavior.
If a nominator chooses a bad validator, they are subject to loss of stake, the main difference between the more common delegated proof of stake system used in many other blockchains. Several on-chain voting mechanisms must agree on changes to the protocol, and a super-majority threshold and batch approval voting are necessary. Having a multilayered governance model opens up the possibility of protocol updates without resorting to a hard fork.
Polkadot’s Governance Roles: GRANDPA
Governance in a blockchain is done through consensus, a method of agreeing to a shared state. All nodes in a network must agree and come to a consensus for the blockchain to continue building and moving forward.
Polkadot takes a different approach to consensus mechanisms using GRANDPA, which stands for GHOST-based Recursive Ancestor Deriving Prefix Agreement, providing Polkadot with more security, scalability, and resiliency. It allows networks to pool security, combining all added protections and applying them to the various chains.
https://polkadot.network/technology/
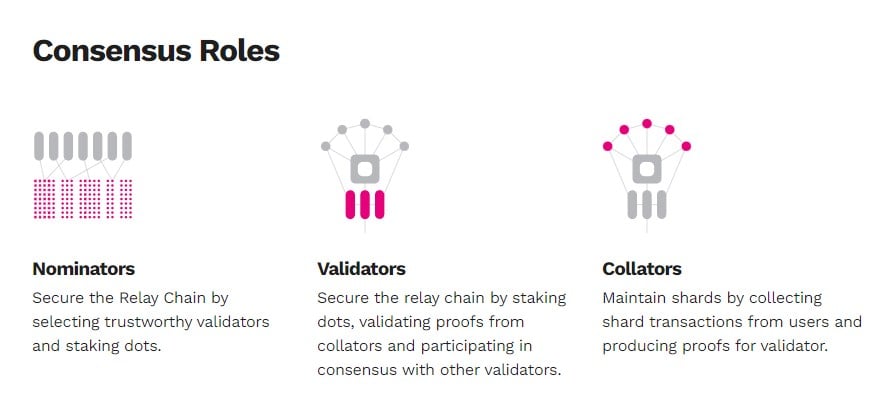
Consensus Roles for Polkadot
- Nominators – Nominators secure the Relay Chain by selecting trustworthy validators and staking DOT, the native coin for Polkadot, in the system.
- Validators – Validators also secure the Relay Chain, but they do it by staking DOT, validating transactions, and participating in consensus with other validators on the network.
- Collators – Collators maintain shards by collecting sharded transactions from users and producing proofs of transactions for validators.
- Fishermen – Fishermen monitor the network and report bad behavior to validators. Collators and any full-node parachain can perform the role of a fisherman in the network.
Polkadot vs. Other Blockchains
| Polkadot | Ethereum | Bitcoin | Cardano | |
| Key goal(s) | Interoperability | Smart contracts and dApps. Defi platform. | Monetary system | dApp platform with peer-reviewed research. |
| Consensus | NPOS (Nominated Proof-of-Stake.) | Proof-of-work, switching to POS. | Proof-of-work | Proof-of-stake |
| Major properties | Scalable with secure cross-chain interoperability. | Security, with less scalability. | Very secure. High energy consumption. | Secure, scalable, and eco-friendly. |
| Token/coin | DOT | ETH | BTC | ADA |
| Date founded | 2016 | 2015 | 2009 | 2015 |
| Founder | Dr. Gavin Wood | Vitalik Buterin | Satoshi Nakamoto | Charles Hoskinson |
What are the Advantages of Polkadot?
While there are a lot of advantages to Polkadot, the following list makes up some of the biggest ones that have attracted so much investment.
- Shared security – Shared security means that all DOTs staked in the system are backing all projects in the ecosystem. This allows for quick deployment instead of building up security and consensus mechanisms for each parachain built.
- Development tools – Polkadot boasts some of the best development tools in crypto. For example, parachain development kits (PDKs) have reduced the time it takes to launch a fully functional blockchain from years to as little as a few days, depending on the situation.
- On-chain governance – Polkadot features on-chain governance that makes upgrading the chain much more straightforward. On Polkadot, the governance process allows for a dynamic blockchain to evolve without a hard fork.
- Crowdloan – Polkadot features crowd loan functionality tied in with the governance functionality. This allows for quick frictionless liquidity and can decentralize much of the protocol’s tokens.
What are the Disadvantages of Polkadot?
While Polkadot shows a significant amount of promise, nothing is perfect, and there are things to be aware of when looking at this ecosystem.
- Competition – Competition is a significant problem for general-purpose smart contract proof of stake blockchains. Tezos, Cosmos, and Cardano compete for the same use case. Ethereum is also in the same neighborhood and is well entrenched.
- Previous hacks – Polkadot has been hacked twice, draining millions of dollars before being fixed. Whether or not there are further vulnerabilities has yet to be proven.
- Limited parachain slots – There are a limited number of slots available for new parachains. This could price out some smaller projects.
Is Polkadot a Good Investment?
Polkadot can be a good investment, but it can be one of many investments that make up a solid crypto portfolio. Polkadot is an ecosystem that attracts a lot of attention, which is one of the significant demands for economic performance, and, therefore, should attract more investment.
However, you should keep in mind that crypto is a relatively new field of development and investment, so, therefore, you should never have all of your money in one coin. A well-diversified portfolio of some of the largest crypto makes a significant amount of sense, and Polkadot certainly falls within that purview. DOT is traded as a CFD as well. Exnes Market View allows you to take advantage of the price movement in this market without relying on keeping custody of the coins themselves. It simplifies the entire process, allowing you to focus on market movement.
Conclusion
Polkadot is an ecosystem that shows a lot of promise. Adoption has been very vibrant, but it should also be noted that there may come a time when Polkadot will have to address the limited slots. That being said, the mass adoption of Polkadot seems to be well underway, and the ability for specific chains to do specific tasks and interact with each other could bring in a whole new world of transactions.
The ability of the ecosystem to govern itself is another attractive feature, and there will likely be more work done on that end as well. The Polkadot network could morph into an industry-specific network, allowing each chain to have its privacy and the ability to communicate and transact with each other openly and honestly. For example, Polkadot would make an excellent banking solution.
The crypto world is young. There is no guarantee on anything, but Polkadot certainly seems as if it will have an exciting future. It could be a “niche system” unless the parachain slots are not addressed. Watch for news on this end because if they open up more use cases and slots, this should bode well for Polkadot over the long term.
What is Polkadot used for?
Polkadot developers can design both private and public blockchains and bridge them to each other via its shared connectivity layer. Chains can choose between their validator set or use the pooled security system of Polkadot to verify transactions via the Relay Chain.
How is Polkadot different from Ethereum?
There are some similarities between the two, as both aim to be widely used platforms for distributed finance and smart contracts. However, Polkadot helps developers build their blockchains and integrates them.
Is Polkadot a cryptocurrency?
Polkadot is both a cryptocurrency and a network. The native coin for the network is called “DOT,” for short.
Is Polkadot a private blockchain?
Polkadot is a network of blockchains, including its main blockchain, known as the “Relay Chain,” and many user-created parallel chains, also known as “parachains.” It also contains a connecting layer that allows the transfer of value and data between most blockchains.
Should I buy Cardano or Polkadot?
In a nutshell, both are excellent ecosystems. If you want to start a crypto portfolio, both Polkadot and Cardano are good choices. The world of crypto is relatively new, so one cannot know which of the networks will last with any absolute certainty.