Scalability and interoperability have been two significant problems for the blockchain world. There are a handful of options for interoperable blockchain networks, with Cosmos being one of the more popular choices. Its Tendermint consensus mechanism and open-source developer tools make it attractive for developers.
What Is Cosmos? – Definition & Meaning
Cosmos touts itself as being the Internet of blockchains, as it is a decentralized network of independent and interoperable blockchains that can exchange information and tokens in a permissionless environment.
The goal of Cosmos is to tackle the same issues most other blockchain projects do, including scalability, usability, and governance, by providing an ecosystem and tools that will help developers quickly build independent blockchains, allowing various use cases and the communication between these blockchains in the network with each other.
Each independent blockchain is called a “zone” in the Cosmos ecosystem and is powered by the Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus algorithm by Tendermint. This is a proof-of-stake consensus, allowing the network to reach an overall consensus, even if some nodes fail or act maliciously. The first blockchain on the Cosmos network is called the Cosmos Hub, with ATOM being the native token of the Cosmos Hub.
What is the ATOM token?
ATOM is the native coin for the Cosmos network with three primary use cases.
- Users pay their transaction fees using ATOM in proportion to the required computational power.
- ATOM is used to participate in the Cosmos Hub governance system. The more ATOM you hold, the more voting power you have in the platform decisions.
- ATOM is the coin staked behind validators, earning them rewards for participating in the consensus algorithm.
ATOM was part of an Initial Coin Offering and had an unlimited supply limit. This makes it an inflationary coin because Tendermint Core rewards those who stake with freshly minted ATOM. The inflation rate of ATOM is adjusted in real time based on the amount staked and the number of those staking.
Cosmos (ATOM) History
Before the Cosmos ecosystem was a reality, blockchain software architect Jae Kwon founded Tendermint, also known as All in Bits Inc., in 2014 and created Tendermint Core. This blockchain engine makes proof-of-stake consensus algorithms. In 2015, Kwon then went on to refine the Tendermint consensus algorithm with the help of Ethan Buchman, which now powers Cosmos. In 2016, the Cosmos white paper was published.
In 2017, the Interchain Foundation, a Swiss nonprofit formed to support the development of the Cosmos network, conducted an initial coin offering of the ATOM token. The ICO raised $16.8 million in 30 minutes, a hugely successful fundraising event.
Two years later, Tendermint raised $9 million in a Series A funding round for the project’s development. Initially, Tendermint had anticipated going the way of enterprise blockchain, selling it to large corporations, but then decided to focus on the ability of the Cosmos network to create many sovereign blockchains and allow people to control their network with on-chain governance.
Who is Behind the Cosmos Ecosystem?
Cosmos was developed via cooperation between different teams. Most of the primary funding for its development was allocated by the Swiss Interchain Foundation, a nonprofit organization that supports and funds open-source blockchain projects, and the Tendermint team.
Software developers Jae Kwon and Ethan Buchman co founded the Cosmos network in 2014 while also creating Tendermint, the consensus algorithm that powers the Cosmos network. The two developers wrote and published the Cosmos white paper in 2016, releasing its software in 2019.
In 2017, the Interchain Foundation held a two-week Initial Coin Offering of the ATOM token, raising just over $17 million. Two years later, Tendermint raised $9 million in a Series A funding round, further pouring money into the ecosystem. Jae Kwon left the project the following year, but Ethan Buchman stayed on board.
In February of 2022, Tendermint, the company, was rebranded by Ignite. It is in the process of splitting into two entities: Ignite and NewTendermint. Kwon returned to NewTendermint in 2022.
How Does Cosmos (ATOM) work?
Cosmos network is an expanding ecosystem of applications and services that are interconnected. It uses hubs, the Tendermint consensus algorithm, and the Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol, sometimes abbreviated as IBC, to ensure that blockchains can communicate with each other securely.
Some of the platforms in the crypto world communicate with each other using smart contracts while locking tokens in one platform, with the asset’s corresponding amount minted on the other. This is an example of using wrapped tokens.
Instead of sending one coin from blockchain A to blockchain B, the token from blockchain A gets locked in a functional blockchain that provides the service. The corresponding amount in a wrapped token is issued and pegged tokens on another blockchain.
On the other hand, Cosmos offers open-source tools to allow developers to build decentralized and sovereign blockchain applications called “zones.” These zones are used instead of relying on one single chain. The zones are the smart contracts on Cosmos. The software development kit (SDK) released by the Cosmos team allows developers to build the zones faster, simpler, and cheaper than other platforms, such as Ethereum. This minimizes the complexity by offering the most common functionality among blockchains, such as staking, governance, and tokens, through simple software development programs. Developers have the freedom and flexibility to change features by adding or subtracting plug-ins and hard-coding their own.
What are Cosmos Hubs?
Each zone (sovereign blockchain) connects to other zones through hubs on the Cosmos network. While Cosmos Hub is the main one, there are other ones available to use.
Each new zone is linked to the Cosmos Hub, but other zones or hubs do not necessarily have to work with each other. The Cosmos Hub, the initial blockchain locked on the Cosmos network, keeps a record of each zone’s state and vice versa.
Zones can function autonomously, authenticating records, transactions, and accounts. They also can create and distribute new tokens and execute blockchain changes.
While Cosmos Hub facilitates interoperability between all zones within the network and keeps track of their states, it also allows interoperability with proof-of-work blockchains like Bitcoin through bridges. This is true even if they do not meet the requirements of the Cosmos protocol.
Tendermint Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) on Cosmos
The Cosmos SDK tools use the Tendermint Byzantine fault tolerance engine consensus protocol by default to secure the network. However, other consensus protocols can be used. Tendermint BFT allows developers to build their own blockchains without coding them from scratch, takes care of validating transactions, executing blocks to the blockchain, and uses a protocol called the application blockchain interface to connect to applications.
The Tendermint BFT functions through a proof-of-stake governance mechanism that supports integrating the distributed network on Cosmos Hub. Participants in the network can stake ATOM and earn rewards. The top 100 stakers can become validator nodes to power the blockchain and vote on changes. Voting is done in proportion to the amount of ATOM state.
Users of the network also delegate their tokens to validators and interchange them. This incentivizes the validator nodes to perform their work honestly. Users can switch between the validators they delegate their ATOM to, depending on their voting needs or desires. The hubs and zones on the Cosmos network communicate through the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol.

Source: cosmos.network
Why is Tendermint important?
Tendermint BFT is popular due to several main reasons:
- Suitability for both public and private blockchains: Tendermint BFT deals solely with the networking and consensus layers of Cosmos blockchains. It gives an outline of how validators interact and agree on transactions. However, developers can still customize the application layer. Each zone can choose how validators are selected and if the blockchain is public or private.
- High performance: Tendermint BFT is a block time of approximately one second and can process thousands of transactions.
- Immediate transaction finality: Transactions are confirmed as soon as a block is created, generally one second or two.
- Security: If the blockchain forks to create a couple of different transaction histories, it’s easy to hold accountability and secure why it happened.
What is the Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol
The Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol, or IBC, is a protocol that allows secure messages to be transmitted between heterogeneous blockchains, called “zones,” and connects them to the Cosmos hub. The process enables users to exchange assets and data securely and freely across sovereign and decentralized blockchains.
The Cosmos Hub is regarded as a service provider to the sovereign chains that must connect to it to become interoperable. Because of this, any sovereign blockchain with different applications, validators, and consensus mechanisms will still communicate with each other and exchange data. Cosmos blockchains can do almost anything they want using the IBC protocol, from cryptocurrency to nonfungible token transfers and smart contracts across various chains.
Cosmos vs. Polkadot
Cosmos and Polkadot use similar governance, but there are some significant differences between them. Governance, transaction validation, and the transfer of tokens or assets between the systems.
Cosmos hub protocol defines that the transactions in the ecosystem are validated by the top 100 validators that stake the most ATOM. Delegators can choose and change validators’ pools to state tokens and earn rewards at any time.
In Polkadot, parachains are somewhat similar to the Cosmos blockchain zones. However, they share identical validators, ensuring a unified and strengthened security across the network through the Relay chain, the central coordinating blockchain on Polkadot. In Cosmos, blockchains connected to the hub do not rely on the same unified security.
Cosmos vs. Ethereum
While Ethereum developers are switching over to proof-of-stake, there are still significant differences between Cosmos and Ethereum. Scalability is an essential issue for Ethereum, causing transactions to be much slower, sometimes taking hours when the network is congested.
Cosmos uses the Tendermint BFT proof-of-stake algorithms that can handle up to thousands of transactions per second, making the process of data and value transfer across the Cosmos ecosystem much faster and cheaper than Ethereum’s gas fees.
Ethereum uses permission smart contracts with specific functions to build the entire ecosystem. In Cosmos, each smart contract or application is essentially a blockchain itself, meaning that they will not interfere with each other while creating a frictionless transaction process.
What are the Problems Cosmos solves?
The main objective of the Cosmos network is to enable communication between all blockchains while solving the three major problems with blockchains in general: sovereignty, scalability, and sustainability.
Sovereignty on Cosmos
The software development kit for the Cosmos network allows developers to build sovereign blockchain applications without ongoing costs. These blockchains can easily interconnect without relying on smart contracts to exist on a different blockchain, making transaction fees smaller due to a lack of network congestion while developing scalability features.
Functionalities on the network could see a lot of innovation, especially in places like decentralized finance, NFTs, gaming, social networks, marketplaces, and any economy that relies on the Internet. Decentralized autonomous organizations are also attracted to Cosmos due to its sovereignty.
Scalability on Cosmos
Cosmos interoperability is what guarantees the ability of a scalable system. Using the Cosmos interoperability model of shared communication standards, any blockchain will be able to communicate with another blockchain and contribute to the evolution of its protocol design.
By duplicating a blockchain to relieve congestion or splitting the apps into multiple application-specific blockchains, interchain token transfers allow multiple chains to communicate on one network.
Sustainability of Cosmos Network
As the Cosmos network uses proof-of-stake to secure the network, the carbon footprint is 99% lower than proof-of-work consensus algorithm-based networks like Bitcoin.
What Are the Advantages of Cosmos?
Cosmos has several advantages over other ecosystems. The main benefits of Cosmos are as follows:
- Adoption: Some major blockchains and dApps, such as Binance Chain, are integrating with the Cosmos network. As of Q2 2022, there are roughly 290 apps.
- Cosmos Software Development Kit: The SDK is a modular framework that simplifies the creation of secure blockchain applications on top of the consensus mechanism called Tendermint BFT.
- Inter-Blockchain Communication: Enables over 150 Tendermint-based blockchains to be interoperable and send tokens/information to each other.
What Are the Disadvantages of Cosmos?
Nothing is perfect, and Cosmos is no different. The crypto world is still young, and there will constantly be growing pains.
- Activity is concentrated: While the IBC has seen adoption grow significantly since it came online in February 2021, out of the roughly 45 apps, 80% of the activity on the network happens in just a handful of zones: Osmosis, Terra, Cosmos, Crypto.com, and Juno.
- Competition: There are a lot of competitors to Cosmos. Polkadot and Ethereum are well-known ecosystems, and Cosmos has issues with brand name awareness.
- Potential regulatory concerns: While the SEC has recently commented that it didn’t look at Ethereum as a security, you cannot assume that they will feel the same about Cosmos, as the entire crypto industry is being looked at.
Is Cosmos a Good Investment?
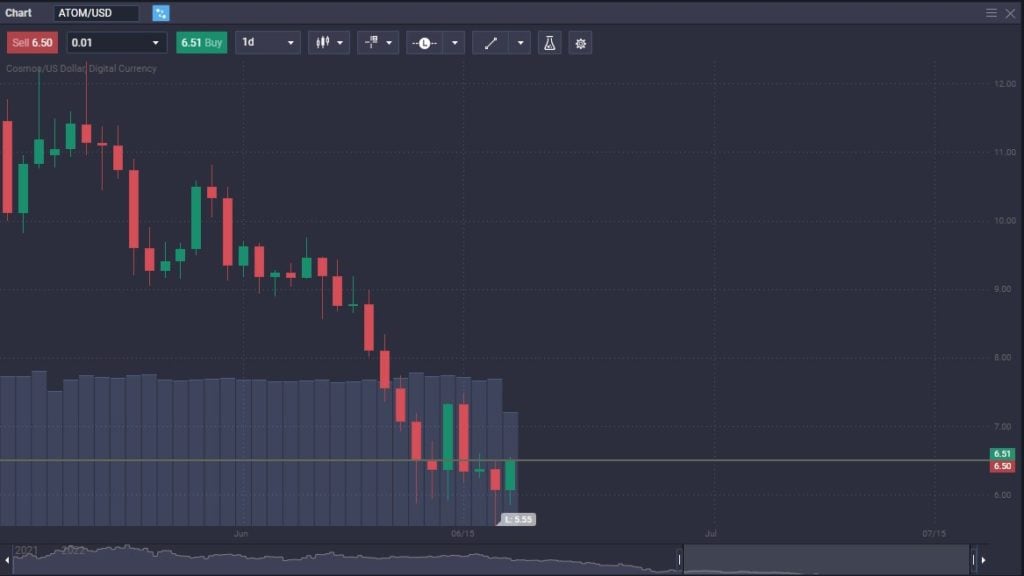
Cosmos certainly has a lot of potential for the long term. However, it would help if you kept in mind that ATOM will be very volatile along with the rest of crypto. The ability to have sovereign blockchains securely communicate with each other is attractive to developers, so, therefore, there should be longer-term interest.
However, remember that it should be part of a well-balanced crypto portfolio to absorb some of the volatility that comes with all crypto, not just ATOM.
Conclusion
Cosmos certainly is an exciting project, and it is more likely than not to have a future that developers will be attracted to. The ability to put together modules and build a blockchain that can be either public or private is desirable. This cuts down most development issues, allowing these developers to build very quickly.
The ability for various “zones” to communicate with each other, regardless of what they do internally, is a huge advantage. However, there are many concerns about brand-name recognition, and therefore, like much of the crypto world, a lot of this is going to, unfortunately, come down to “hype.”
This is an ecosystem that a lot of developers like, so with that being the case, it is very likely that sooner or later, we will start to see even bigger projects in the ecosystem. However, it would help if you never went “all in” when it comes to any crypto, and Cosmos will be no different. Because of this, you may be better served trading the CFD market, taking advantage of shorter-term price fluctuations as you can at Exnes Market View.
What is Cosmos used for?
Cosmos quickly lets designers build custom, secure, scalable, and interoperable blockchain applications. As Cosmos allows blockchains to maintain sovereignty, process transactions quickly, and communicate with other blockchains in the ecosystem, it has become popular with developers.
What is Cosmos based on?
Cosmos is based on the consensus protocol called Tendermint, created by Jae Kwon in 2014. This protocol allows for the interoperability, sovereignty, and security found throughout the Cosmos network by each participating “zone.”
Does Cosmos crypto have a future?
Like everything else in cryptocurrency, the future is difficult to forecast. It will come down to whether or not other developers choose to jump on board and whether or not there is a “killer app” that is found on the network. However, it’s worth noting that Cosmos does solve several problems.
Is Cosmos a token or coin?
The native token of the Cosmos network is ATOM.
Is cosmos crypto inflationary?
Yes, it is. This is because new ATOM is minted for those who choose to stake on the system. In theory, the supply of ATOM could be unlimited.