Chainlink is a cryptocurrency and technology platform that is best thought of as “middleware.” It connects non-blockchain Enterprises with some of the biggest blockchain platforms. This allows for enterprise-sized solutions for data from multiple sources.
Chainlink has its currency, LINK, to reward node operators. Chainlink is built on the Ethereum platform but offers functionality through multiple blockchains.
Who Invented Chainlink?
Chainlink was invented by the current CEO, Sergey Nazarov, and current CTO, Steve Ellis. Created in 2017, the duo co-authored a white paper on the protocol and network with Cornell University professor Ari Juels.
Chainlink History
Chainlink was created in 2017 and raised $32 million in an Initial Coin Offering that created 1 billion LINK tokens. In late 2018, Chainlink then acquired TownCrier. Chainlink increased its potential by the acquisition, as it allows the Ethereum blockchain to interact with web sources that use HTTPS.
Chainlink was launched on the Ethereum mainnet in May 2019. In the following year, Chainlink integrated DECO, a Cornell project co-created by Juels. Its authors describe it as a protocol that uses zero-knowledge proofs to allow users to provide information to a blockchain oracle without revealing sensitive information such as birthdates.
By February 2022, Chainlink had secured more than $60 billion in deposits via smart contracts and was used by 1100 projects.
What’s So Special About It?
Chainlink allows the blockchain world to interact with the outside world. Chainlink offers a “bridge” between blockchain networks and the points where data comes into the blockchain. These areas have long been areas of concern, as data can be manipulated, compromised, or falsified.
Chainlink prioritizes three principles: distribution of data sources, distribution of oracles, and the use of trusted hardware.
How does Chainlink Differ from Ethereum?
The Chainlink network should be thought of as complementary to the Ethereum network and other blockchains. Chainlink allows secure communications between Ethereum network projects and off-chain data. This will enable projects to interact with such examples as stock prices, football scores, weather, etc.
Ethereum tokens are used to spend on purchases, facilitate smart contracts, and reward miners and validators on the Ethereum network. Chainlink tokens are used to pay node operators on the network, giving them a single-use.
Both operating protocols use proof-of-stake, offering another similarity. LINK is the native token for the Chainlink network; it is built on the Ethereum platform, making them compliant with its protocols.
How does Chainlink Work?
Chainlink uses a network of decentralized nodes (oracles) that provide off-blockchain information and data to the more extensive network. The network’s structure eliminates reliability issues to collect data as trustworthy and accurate as possible from the outside world.
A smart contract will request data from the Chainlink network and is referred to as the Requesting Contract. The Chainlink protocol will respond by creating a Service Level Agreement, or SLA, consisting of three separate contracts.
The first contract is the “Reputation Contract.” Each node is given a reputation score. The reputation contract checks the track record of the node to verify performance history and a description of authenticity. Unreliable nodes are sorted out.
The second contract is the “Order Matching Contract.” This contract delivers the data request to Chainlink nodes. Nodes place bids for the requested data. The contract selects the correct number of nodes and can provide the requested data. Users can request specific nodes to provide data.
The third contract is the “Aggregating Contract.” Once the selected nodes for the information have requested data through external sources, the Chainlink software will translate the data into blockchain language. It then validates the data from every source and compares multiple sources.
Because of this process, Chainlink has provided a way to efficiently source reliable and accurate off-chain data for smart contracts to use in various cases.
Does Chainlink Have a Currency?
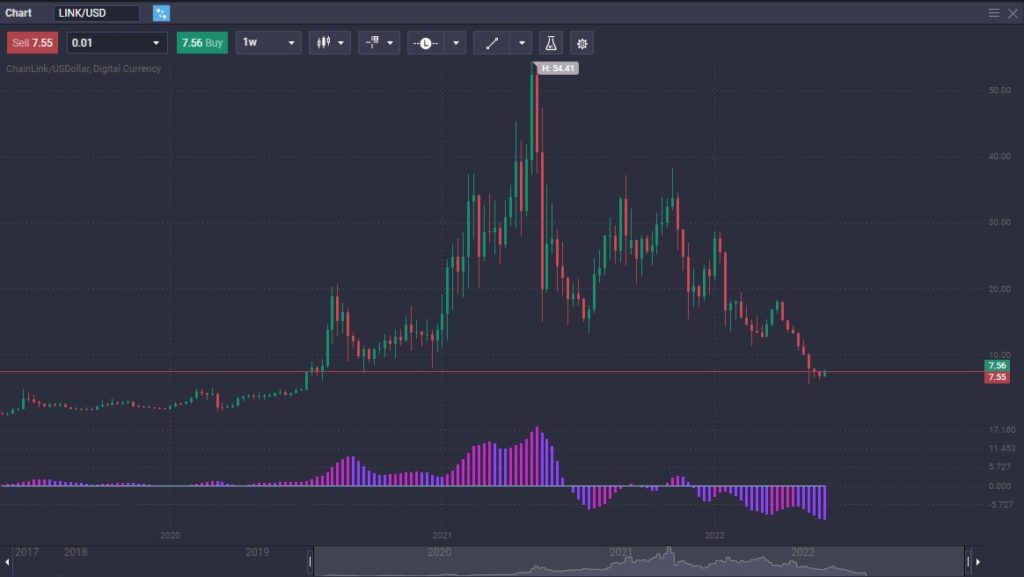
Yes, it does. LINK is the cryptocurrency for the Chainlink network. LINK has a total supply of 1 billion tokens, with 35% of these sold during the ICO in 2017, and about 55% of the tokens are still in the hands of its founders.
LINK does not have a mining process, nor does it mint new tokens as a reward for staking. Its supply is fixed, and will not change, thereby avoiding inflation.
LINK is the only currency that can interact with the network, meaning that smart contracts that wish to obtain data from the Chainlink network will have to use LINK to pay node operators for their services. Node operators determine prices for their services based on the demand for the data requested.
Node operators stake LINK to provide data to the network. The deposited LINKS demonstrates a commitment to the network and incentivize good behavior. A reputation score goes along with being a node operator, and the size of its stake, among other factors, will increase or decrease the reputation score. This is thought of as a sign of the likelihood of receiving quality service.
LINK is an ERC-667 token running on the Ethereum network, with similar functionality as the more common ERC-20 token. You can store LINK on most Ethereum wallets.
Why Does LINK Have Value?
The blockchain world is relatively young, and therefore vast amounts of information are not recorded on it. Furthermore, there will always be a use for a “bridge” between on-chain and off-chain. As Chainlink interacts with oracles, they do not operate on its blockchain; it allows more information transfer.
The cryptocurrency LINK has value because it has to be used by those wishing to make transactions. As there are so many opportunities to pull information into the blockchain from other places and, of course, vice versa, the value of LINK should continue to increase as long as blockchain use increases.
How Do You Get Ahold of Link Tokens?
The LINK tokens are ERC-677 tokens, inheriting functionality from the ERC-20 token standard, allowing for token transfers to contain data. You can buy these tokens at many major exchanges. These tokens can be stored on any Ethereum-based wallet. If you are looking to simply benefit from price movement, the CFD markets at Exnes Market View are the easier and quicker solution.
What Can You Do With Chainlink?
Chainlink allows Oracle services on Ethereum, Bitcoin, and other blockchains. Developers in large companies consult data as node operators to the network and are paid LINK tokens. This means that it can serve as a repository for enormous amounts of data for end-users.
The network allows computations on and off the blockchain, supporting what it refers to as “hybrid smart contracts.” Enterprises that use Chainlink have access to major blockchain networks, allowing mass adoption of blockchain solutions.

https://chain.link/data-feeds
Goals of Chainlink
Chainlink continues to grow by expanding its support for blockchain environments and offering new use cases for its “hybrid smart contracts.” As massive amounts of data and records are not stored in the blockchain yet, Chainlink should have plenty of use case scenarios as the on-blockchain, and off-blockchain worlds interact.
In 2021, the network secured more than $75 billion of value as it grew to include 1100 projects. Out of the 1 billion tokens that make up the maximum supply, 467 million have been issued as of spring 2022.
What is an oracle Chainlink?
Oracles are entities that connect blockchains to external systems, which allow smart contracts to execute based upon inputs and outputs originating from the blockchain.
Is Chainlink partnered with Oracle?
Yes, Chainlink and Oracle have partnered to help startups use Chainlink’s decentralized Oracle tech to monetize APIs via smart contracts on the Oracle Blockchain Platform.
Is Chainlink oracle free?
No. Each service has its own price.
What is an oracle Chainlink address?
The oracle Chainlink addresses a string of characters that will point the user to a specific process or collection of data to be used on the blockchain. This includes information from the outside world.
Does Chainlink have a future?
Yes, more likely than not, it does have a future. One of its most significant benefits will be pulling information from outside of the blockchain for users to implement. In a sense, Chainlink is trying to bring a collaboration between the real world and the blockchain world.
Why is Chainlink so important?
Allowing data collection from external sources opens up much more functionality when it comes to blockchain applications.