When comparing Chainlink vs. Polkadot, there are many things to remember. Both Chainlink and Polkadot are popular projects, and they do serve some similar uses. However, significant differences need to be kept in the back of your mind, which is the central theme of this article. Sometimes, it’s not a question of “Polkadot vs. Chainlink” but rather understanding the use case scenario for both in making them valuable to investors. These standard ERC-20 tokens have exploded in popularity over the last few years, so it is worth investigating.
Сhainlink: The basics
To make trading decisions in Chainlink and Polkadot, you need to know the basics about each coin. In this section, we look at Chainlink.
What is Сhainlink, and how does it work?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides data to smart contracts on blockchain platforms like Ethereum. It aims to secure smart contracts by allowing them to access data from various sources off-chain and integrate it into the blockchain.
A smart contract can request data through a Chainlink node, which will then retrieve the data from a data source and return the result to the contract. The data is verified by multiple Chainlink nodes, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the data before the smart contract uses it. The network is secured by staking and a decentralized network of node operators.
Advantages of Сhainlink
Chainlink offers several advantages, including:
- Decentralization: Chainlink operates on a decentralized network, meaning that there is no central point of failure, and no single entity can control the data being used by the network.
- Security: Chainlink verifies data from multiple sources, making it more secure and trustworthy than data from a centralized source.
- Interoperability: Chainlink allows for easy integration with various data sources and blockchain platforms, making it highly interoperable.
- Reliability: The decentralized nature of Chainlink ensures that the network is always available and that data can be reliably and accurately retrieved, even if individual data sources become unavailable.
- Scalability: Chainlink is designed to be scalable. It can handle large data requests and maintain fast response times, making it well-suited for large-scale decentralized applications.
- Cost-effectiveness: Using Chainlink can help reduce the costs associated with data acquisition and management, as it eliminates the need for centralized infrastructure and reduces the risks of data breaches and downtime.
Disadvantages of Сhainlink
Chainlink, like any technology, has its limitations and challenges, including:
- Complexity: The technology behind Chainlink can be complex and challenging for those with limited technical knowledge, making it difficult for some users to utilize its capabilities thoroughly.
- Adoption: While the use of Chainlink is growing, it still has limited adoption in the wider blockchain and DeFi space, and more work needs to be done to educate users and encourage wider adoption.
- Dependence on Ethereum: Currently, Chainlink is built on the Ethereum blockchain, which depends on Ethereum’s stability and scalability. This could limit its potential for use in other blockchain ecosystems.
- Volatility: The price of Chainlink’s native token, LINK, is subject to significant volatility, making it a risky investment for some users.
- Competition: Other oracle solutions are emerging in the blockchain space, and Chainlink will need to compete with these solutions in terms of features, security, and adoption to maintain its position as a leading oracle solution.
- Regulation: The regulation of decentralized finance and blockchain-based solutions is still a developing area, and regulatory changes could impact the use and adoption of Chainlink in the future.
Polkadot: The basics
To make informed decisions on buying Chainlink and Polkadot, you need to know the basics. In this section, we look at Polkadot.
What is Polkadot, and how does it work?
Polkadot is a blockchain platform that enables interoperability between different blockchain networks. It aims to allow for the transfer of data, assets, and even full blockchain systems between other blockchains. This is what is known as having a cross-chain bridge. It also has the distinction of having application-specific blockchains.
Polkadot consists of multiple parachains (parallel chains) that are connected to a central relay chain. Each parachain can operate independently and have its consensus mechanism while also being able to communicate and exchange data with other parachains. This allows for the creation of a multi-chain ecosystem where different blockchains can interact and exchange value with one another securely and seamlessly.
In Polkadot, validators are responsible for securing the network and verifying transactions. They are incentivized to do so through rewards paid in the platform’s native token, DOT.
In summary, Polkadot is a blockchain platform that enables interoperability between different blockchains, creating a multi-chain ecosystem where other blockchains can securely and seamlessly interact and exchange value.
Advantages of Polkadot
Polkadot offers several advantages, including:
- Interoperability: Polkadot enables seamless interoperability between different blockchain networks, transferring data, assets, and even full blockchain systems between blockchains.
- Scalability: Polkadot is designed to be scalable, allowing for the creation of a multi-chain ecosystem that can handle a large volume of transactions and data.
- Flexibility: Polkadot’s architecture allows for the creation of a wide range of blockchain applications, from simple token systems to complex decentralized applications, while also allowing for the integration of existing blockchain systems.
- Security: Polkadot’s relay chain is designed to provide a secure and decentralized infrastructure to secure and verify transactions across different blockchain networks.
- Innovation: Polkadot’s architecture allows for the creation g new and innovative blockchain applications and solutions while enabling the integration of existing and proven blockchain technologies.
- Community: Polkadot has a strong and growing community of developers, users, and organizations, which helps to drive innovation and adoption of the platform.
- Decentralization: Polkadot operates on a decentralized network, meaning that there is no central point of failure, and no single entity can control the data being used by the network.
Disadvantages of Polkadot
Polkadot, like any technology, has its limitations and challenges, including:
- Complexity: The technology behind Polkadot can be complex and challenging to understand for those with limited technical knowledge, making it difficult for some users to utilize its capabilities fully.
- Adoption: While the use of Polkadot is growing, it still needs more adoption in the wider blockchain and DeFi space. More work needs to be done to educate users and encourage wider adoption.
- Maturity: Polkadot is a relatively new technology, and its full potential has yet to be realized. It may take time for the ecosystem to mature and full capabilities to be fully realized.
- Regulation: The regulation of decentralized finance and blockchain-based solutions is still a developing area, and regulatory changes could impact the use and adoption of Polkadot in the future.
- Competition: Other blockchain platforms and solutions are emerging markets, and Polkadot will need to compete with these solutions in terms of features, security, and adoption to maintain its position in the market.
- Volatility: The price of Polkadot’s native token, DOT, is subject to significant volatility, making it a risky investment for some users.
- Integration: Integrating existing blockchain systems with Polkadot can be a complex and time-consuming process and may require significant technical expertise and resources.
Key differences between Сhainlink and Polkadot
To make the most of your investment, you should understand that there are significant differences between Chainlink and Polkadot. The question is, “Should I buy Link vs. Polkadot or the other way around?” When comparing DOT vs. LI, you will find many similarities and a few significant nuances in how they operate.
Value
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts to real-world data. It is designed to allow smart contracts to access external data and off-chain resources. It is considered a crucial component for the growth of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem or even the major of DeFi application projects. The value of Chainlink is primarily derived from its utility as a key infrastructure for the DeFi ecosystem and its growing adoption by decentralized applications.
Polkadot, on the other hand, is a next-generation blockchain network that aims to provide a unified network for different blockchain systems to operate and exchange information with each other. It is designed to allow different blockchains to interoperate and share resources, which could increase the scalability and efficiency of the entire blockchain ecosystem. The value of Polkadot is primarily derived from its potential to become a cornerstone of the emerging decentralized internet and its ability to facilitate cross-chain communication and interoperability.
Evolution
Chainlink and Polkadot have both undergone a significant evolution since their inception. Here’s a brief overview of their development:
Chainlink:
2014: The concept of Chainlink was first introduced by its co-founders Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis.
2017: Chainlink launched its Initial Coin Offering (ICO), which raised 35 million dollars.
2018: Chainlink launched its mainnet, which allowed developers to create and run decentralized applications on its network.
2019-2020: Chainlink saw growing adoption and partnerships with major companies and decentralized finance (DeFi) projects.
2021: Chainlink’s popularity and value skyrocketed as the DeFi ecosystem grew and more decentralized applications started to use its oracle network.
2022: Major security upgrades for the system are implemented.
Polkadot:
2016: The concept of Polkadot was first introduced by its co-founder Gavin Wood.
2017: Polkadot raised over 140 million dollars in its ICO.
2019: Polkadot launched its testnet, which allowed developers to experiment and test their decentralized applications on the network.
2020: Polkadot launched its mainnet and started to attract a growing number of developers and projects to build on its network.
2021: Polkadot’s value and popularity grew significantly as the ecosystem of decentralized applications built on its network expanded.
2022: Polkadot embarks on bringing asynchronous backing into the network. This block time of 12 seconds should be brought down to just 6.
Coin Limits
Chainlink has a fixed maximum supply of 1,000,000,000 (1 billion) LINK tokens, the native cryptocurrency of the Chainlink network.
Polkadot has different token economics compared to Chainlink; it has an initial supply of 10^10 (10 billion) DOTs, which will be split into two pools:
80% of the total supply is locked up and gradually released to incentivize long-term network participation.
20% of the total supply is immediately transferable and can be traded on the open market.
What Makes Polkadot and Сhainlink Similar?
To better understand the investments, you need to know where they are similar to each other to understand which one you buy or sell or if you do the same with both.
Mining Process
Chainlink uses a consensus mechanism called “Proof of Stake (PoS),” which allows token holders to validate transactions and earn rewards for doing so. In the Chainlink network, validators are selected to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of LINK tokens they hold and are willing to “stake” or lock up as collateral.
On the other hand, Polkadot uses a unique consensus mechanism called “Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS),” in which validators are elected by token holders to validate transactions and secure the network. In the Polkadot network, validators are chosen based on the amount of DOTs they hold and the number of nominators (token holders who support them).
While there is no simple way to mine Chainlink, it can be done if a node is nominated.
Less Energy
Chainlink and Polkadot use less energy than other cryptocurrencies that use “Proof of Work (PoW)” consensus mechanisms, such as Bitcoin. PoW is a computationally intensive process requiring a lot of energy to perform the complex mathematical calculations necessary to validate transactions and create new blocks.
In contrast, Chainlink uses a “Proof of Stake (PoS)” consensus mechanism, which is less energy-intensive as it does not require the same amount of computational power to validate transactions and create new blocks. Instead of solving complex mathematical problems, validators are selected based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to lock up as collateral.
Similarly, Polkadot uses a “Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS)” consensus mechanism, which is also more energy-efficient than PoW. In the Polkadot network, validators are elected by token holders to validate transactions, and the process of creating new blocks is much less energy-intensive compared to PoW.
Staking
In Chainlink, staking involves holding LINK tokens in a wallet and participating in the PoS consensus mechanism. Validators are selected based on the amount of LINK they have and are willing to stake, and they earn rewards for verifying transactions and creating new blocks. Stakers must maintain a minimum amount of LINK in their wallets to remain eligible for rewards and ensure the network’s security.
In Polkadot, staking involves holding DOT tokens and participating in the NPoS consensus mechanism. Token holders can choose to become validators or to support existing validators by nominating them. Validators are elected based on the amount of DOTs they hold and the number of nominators supporting them, and they earn rewards for validating transactions and securing the network.
Both Chainlink and Polkadot have designed their staking mechanisms to incentivize long-term network participation and ensure the network’s security and stability. By participating in staking, token holders can earn rewards while helping to support the growth and development of these critical blockchain networks.
Polkadot vs. Сhainlink: Comparison
The table below shows a “30,000-foot view” of the two networks.
| Feature | Сhainlink | Polkadot |
| Date Founded | 2017 | 2017 |
| Ticker | LINK | DOT |
| Market Cap | $3.5 billion | $7.8 billion |
| General Purpose | Interoperability between different networks | Transfer of data from custom blockchains w/o exposing sensitive data |
| Mining Standard | Proof-of-stake | Proof-of-stake |
| Maximum Available Supply | 1 billion | 1 billion |
| How Is the Currency Used? | Governance token and staking, as well as transaction fees | Governance token and staking, as well as transaction fees |
| What Influences the Value? | Network growth and general adoption | Demand for the Polkadot network itself |
LINK vs. DOT: Historical Price Action Reviewed
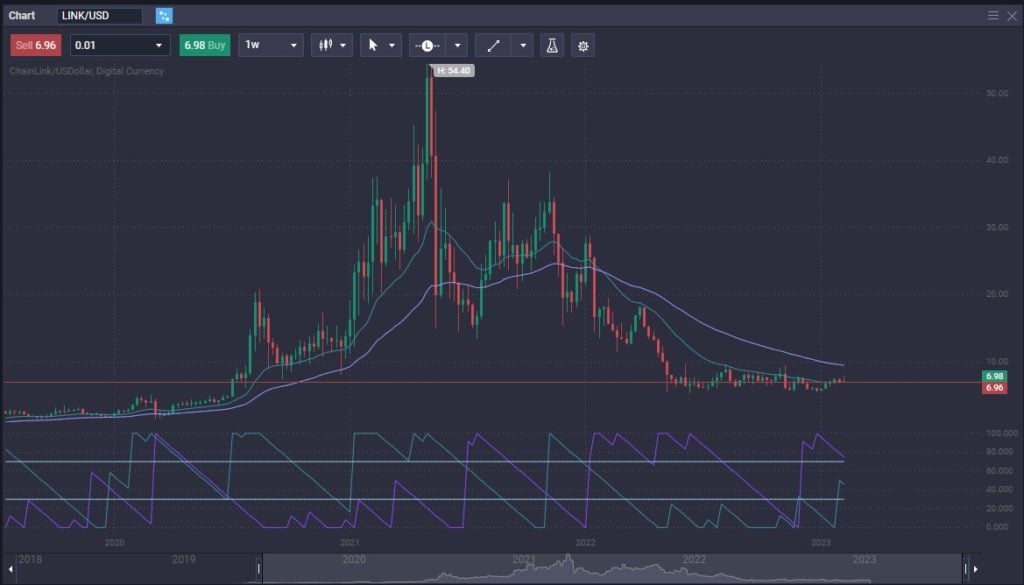
Chainlink trading on Exnes Market View’s world-class platform
The historical price action of both Chainlink (LINK) and Polkadot (DOT) have been volatile and have experienced significant price swings over the past few years.
Chainlink was launched in 2017 and initially had a relatively modest price but saw a significant increase in value in late 2020 and early 2021, reaching an all-time high of over $43 in August 2021. Since then, it has seen s significant decline along with the rest of crypto as we entered “crypto winter.”
Polkadot was launched in August 2020 and experienced rapid growth in its early days, reaching an all-time high of over $45 in January 2021. Like Chainlink, its price has also experienced significant volatility, with periods of rapid price appreciation followed by corrections.
Сhainlink vs. Polkadot: Which one is the better investment?
This is a tricky question to answer because, quite frankly: they both show such promise. However, when investing in cryptocurrencies, you must understand that you are very early in the game. There is no way to know the future, primarily as it is being written quickly. The best way to be involved in crypto is to be diversified and never put all your money into one market.
That being said, both of these coins make up part of a well-balanced crypto portfolio.
Conclusion
When looking at both of these markets, be it Chainlink or Polkadot, both of them make a compelling argument for future adoption. That’s what trading crypto is all about, adoption. Crypto will likely enter its adult phase with a series of specialized blockchains. This is where Polkadot could come in handy as it is quick and has a security system that is essentially “plug-and-play.”
Chainlink is a decentralized Oracle network that provides reliable data to smart contracts, which makes it important if the structure for DeFi. Because of this, it will likely continue to attract much attention as well. Simply put, both of these coins, more likely than not, will be widely used in the future, assuming that crypto adoption continues. That being said, you should also keep abreast of the latest developments in the crypto world because it is so young.
Is Chainlink or Polkadot better?
There is no straightforward answer, as they are trying to serve different purposes. LINK is trying to tie together other networks, bringing them together. The DOT network is an ecosystem with chains that can communicate, keeping sensitive data from being exposed.
Is Сhainlink similar to Polkadot?
No, not really. Chainlink is a network that allows data to be transferred on various blockchain platforms, most notably Ethereum. Polkadot is a multi-chain network that provides interoperability between different platforms, allowing them to exchange data and assets. Polkadot enables the creation of new custom blockchains as well.
What is the difference between LINK and DOT?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides real-world data to smart contracts on various blockchain platforms, including Ethereum. It aims to address the challenge of ensuring the reliability and security of data used in smart contracts.
Polkadot is a multi-chain network that aims to provide interoperability between different blockchain platforms, allowing them to interact and exchange data and assets. Polkadot also enables the creation of new and custom blockchains and allows developers to build decentralized applications (dapps) that can run on multiple blockchains.